Energy Reduction Key to UK cold chain
28th July 2023
The Cold Chain Report 2023, recently published by the UK’s Cold Chain Federation, sheds light on the views of cold chain professionals regarding the future of temperature-controlled logistics. The report is based on a comprehensive survey from Cold Chain Federation members. The report suggests that energy management technologies (Including renewables and battery storage) will have the profoundest influence in this field over the next ten years with 56% of participants ranking this top. The report also highlights that the greatest challenge currently faced by cold chain businesses is the cost of energy and fuels, with 79% if respondents to the survey stating that as the top challenge.
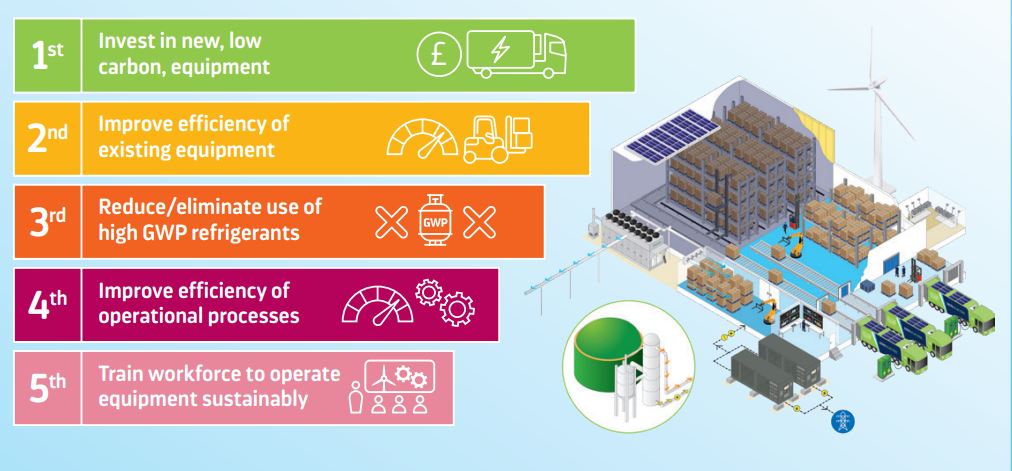
Among the participants in the industry survey, a significant 40% of respondents recognized the importance of investing in new, low carbon equipment as the most critical step going forward. Additionally, 21% of participants underlined the significance of improving the efficiency of existing equipment and reducing or eliminating the use of high GWP (Global Warming Potential) refrigerants, as their top action.
Among the intriguing findings of the survey, one important insight emerges regarding the total carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions associated with cold storage. The report reveals that these emissions amount to 0.42 MtCO2e (million metric tonnes of CO2 equivalent). When examining the sources of these emissions, it becomes apparent that refrigerant leakage accounts for 38.1% of the total, while direct emissions resulting from energy consumption make up the remaining 61.9%, equivalent to 0.26 MtCO2e. This data underscores that to achieve sustainability goals, it is crucial to focus on two critical aspects: minimizing refrigerant leakage and improving energy efficiency.

The Executive Director of the Cold Chain Federation, Tom Southall, commented on the industry’s collective belief in the pivotal role of energy management technologies in the coming decade. He states “There is also a strong feeling amongst business leaders, that whilst energy prices are a short-term headache, the long-term impact will be to bring forward the changing way energy is managed. Whether it be electrification of refrigerated vehicles, harnessing the power of renewables or thinking differently about energy storage and reusing the heat from our warehouses, the opportunities are clear.”
This belief considers not only the anticipation of high energy costs but also the essential transition towards achieving net zero cold chain operations. These measures enable businesses to meet customer requirements but also comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
Furthermore, the Cold Chain Report highlights the proactive response of operators within the industry. Among the 278 members of the Cold Chain Federation, 25% of cold storage sites in the UK have now implemented renewable energy technology, showcasing a commitment to more sustainable practices. In addition to the survey findings, the report provides comprehensive information encompassing the latest facts and figures related to both cold storage and temperature-controlled distribution.
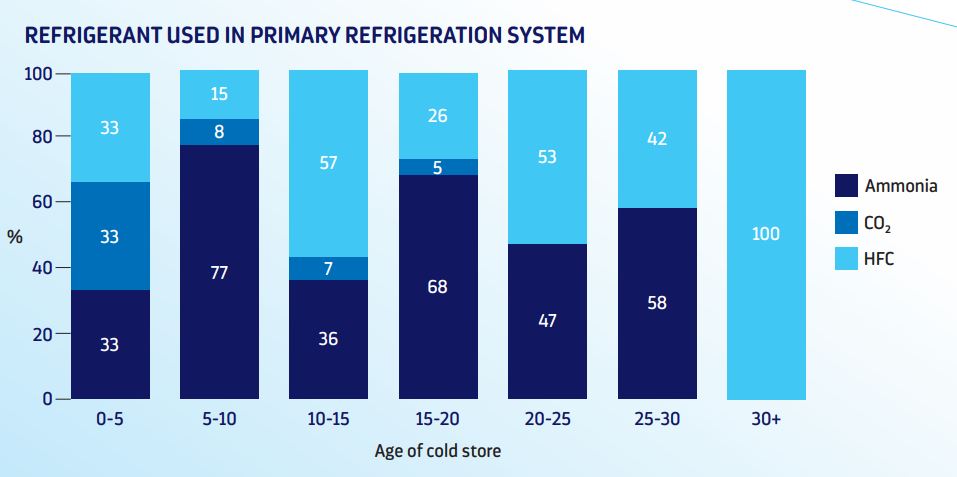
Finally one notable industry shift emphasized in the report is the transition away from ammonia towards carbon dioxide (CO2) as an alternative refrigerant in newer cold stores. According to data from the Cold Chain Federation, the use of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), ammonia, and CO2 is evenly distributed within the cold chain sector.
For those interested in exploring the topic further, the complete Cold Chain Report 2023 can be accessed and downloaded through this link, offering valuable insights into the trends and developments shaping the cold chain industry.


